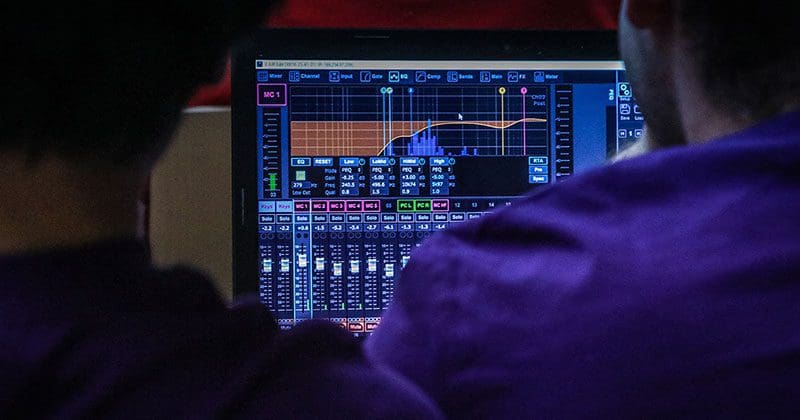
For well more than a decade, respectable mobile enhancement retailers around the world have understood the need for a digital signal processor to be included in any car audio system upgrade. Even if you’ve chosen the lowest-distortion speakers on the planet and your installer has agonized over placement and integration, they still need a way to compensate for the peaks and valleys in the frequency response that come with the confines of a vehicle interior. The same process is used to calibrate home and commercial theater systems, recording studios, clubs and concerts. Let’s look at a few reasons why having a DSP in your system is crucial to achieving realistic sound.
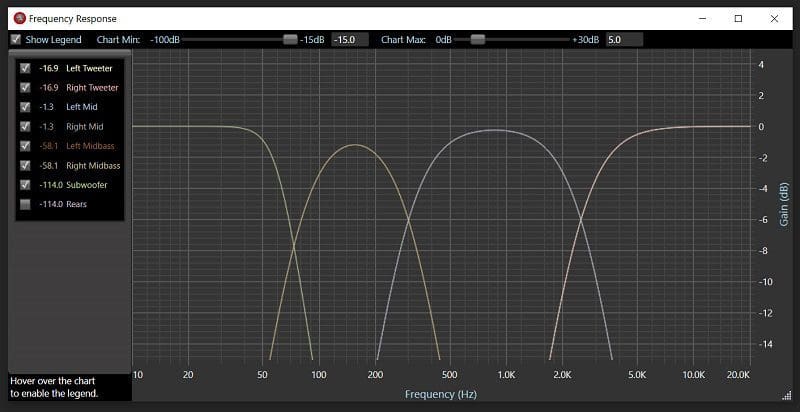
Accurate Crossover Settings
One benefit of having your installer tune your audio system with a DSP as opposed to an analog processor with knobs is accuracy. The potentiometers used on amplifiers and stand-alone processors are notoriously inaccurate. Your installer could turn a dial on an amplifier to a setting labeled 80 Hz and end up with an actual crossover point of anything from 70 to 90 Hz.
Because digital signal processors use mathematical algorithms to alter the audio signal, they are incredibly accurate. Your installer can set a high-pass filter at 2,500 Hz for your tweeters and know that there won’t be any issues with power handling from unwanted midrange energy. The same applies to a low-pass filter at the top of the midrange driver. You don’t want any overlap or underlap (a gap in the frequency response) that could affect frequency response.
Taming Frequency Response Issues
To keep this discussion simple, let’s use a two-way bookshelf speaker on a desk as our reference for measurements. The speaker uses a 5¼-inch woofer with a glass fiber/foam core cone and a hard dome tweeter. Half of an eight-channel amplifier with integrated digital signal processing powers the speakers in a fully active configuration. This last statement means there is a pair of amplifier channels dedicated to the woofers and a second pair dedicated to the tweeters. No passive crossovers are used anywhere in the system. These speakers are used in conjunction with a dedicated subwoofer, so a high-pass filter has been applied at 80 Hz.
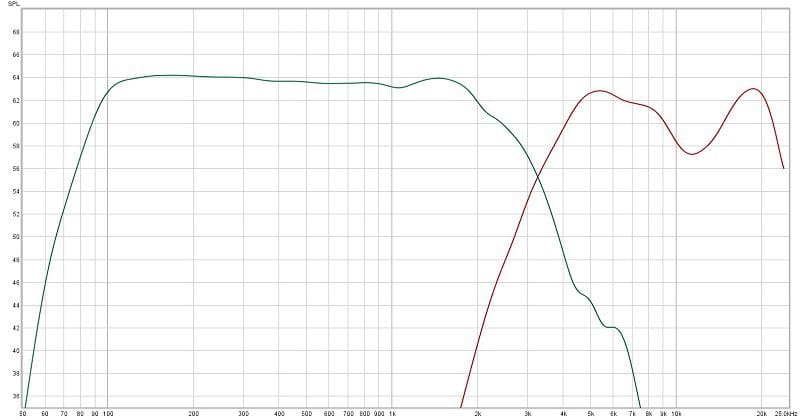
If we measure the frequency response of the woofer and tweeter with the mic close to their respective cones, we see the response curves shown in Graphs 1 and 2. You can see that the response of the woofer is relatively flat, with no significant peaks or dips at any frequency.
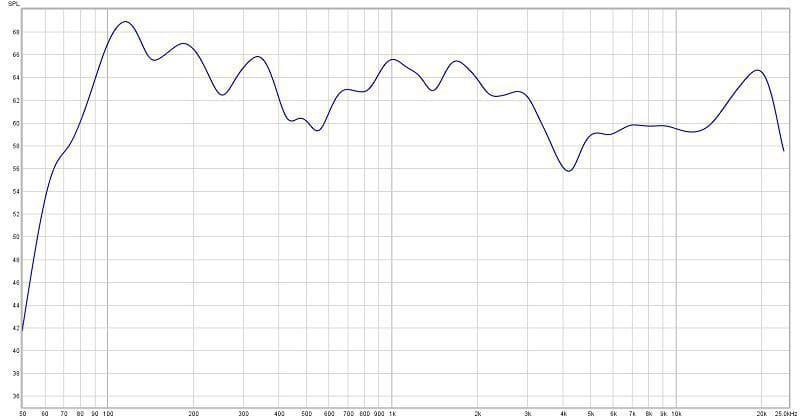
If we take a second measurement (Graph 2) of the entire system (both the woofer and tweeter playing at the same timer) at a distance of one foot from the speaker, we can see that the reflections from the desk and nearby objects have imposed peaks and valleys in the response curve. The deviation is more than 13 dB. These changes add emphasis to specific frequencies, changing the tonal balance of the speaker and detracting from the accuracy of the listening experience.
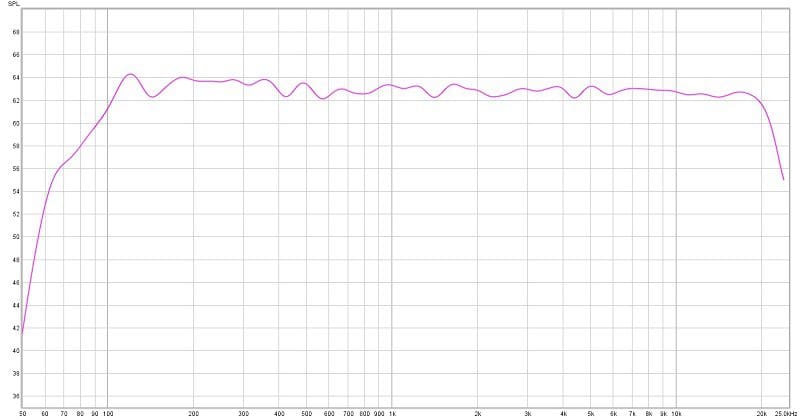
If we apply compensation using the equalizer built into the amp, you can see that the response at the listening position is smoothed. The natural balance of the audio signal is much more realistic at the listening position.
The interior of your vehicle imparts much more significant changes in response because of the abundance of glass, vinyl, plastic and carpet surfaces. Proper equalization is even more important in your car or truck in terms of achieving great audio performance.
Just as with our explanation for the need for accurate crossover settings, using a DSP will allow for precise amounts of equalization. If the system needs a cut of 2 dB at 1 kHz, 4 dB of boost at 320 Hz and 3 dB of cut at 80 Hz, the DSP can deliver with exacting precision and repeatability.
Pathlength Compensation
If the product specialist you’re working with is designing what’s known as a single-seat audio system, then they will want to adjust the output of each speaker in the car or truck so that the sound arrives at your ears at the same time. Compensating means adding delay to the signals going to the closest speakers. Processor calibrations that provide good imaging for both seats are also available, but use a different tuning process with no left-to-right signal delay
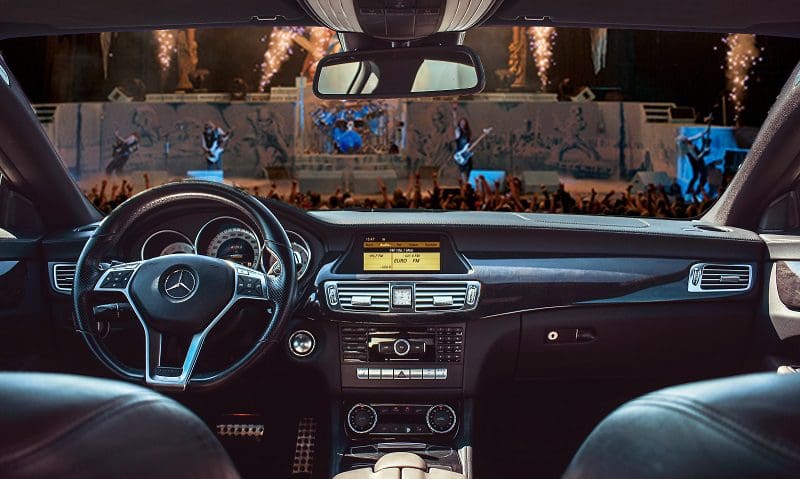

The result, when executed properly, is that the music you hear will seem to come from a point between all the speakers. In most cases, this puts the performance on what’s known as a virtual soundstage that spreads the width of the vehicle. If the equalization process was executed properly, each performer should be placed in their relative position across the stage. This phenomenon is called imaging.
Without compensating for pathlength, the soundstage will be clumped to the left side of the vehicle. This detracts from the realism of the performance. The closer you sit to the speakers in the door, the worse the image pulls to the left.

It should be noted that many people prefer to be immersed in the middle of their music experience. If you prefer a “club” sound, your installer can deliver that with the addition of rear speakers and a modified system calibration process.
System Presets
Many digital signal processors allow for quick access to presets. If your car is set up for a single-seat tune, your installer may create a second preset that removes the signal delay and changes the way the system is equalized. They may also create a preset that provides that immersive club-like sound. This type of calibration can be great if there are passengers in the rear of the vehicle who want to enjoy the music.
Depending on the processor, presets can be loaded using simple analog switches, with a dedicated remote control or with a computerized system controller. The selection method depends on the processor you and your product specialist agree to for your system.

Enjoy Great Sound from Your Car Stereo
If you have an existing aftermarket car audio system or are planning an upgrade in the near future, ask your local specialty mobile enhancement retailer about how adding a DSP and having it professionally calibrated can improve the performance of the system. Few upgrades offer a more dramatic and beneficial improvement to the realism and detail of a mobile audio system.

