We’re back in the lab and working on a few more articles about amplifier specifications in order to wrap up this series. This time, we’re going to talk about the amplifier stereo separation specification. In a nutshell, the stereo separation, or crosstalk, number tells us how much of an audio signal leaks from one channel of an amplifier to the other. Of course, for the number to exist, you need to be looking at a stereo amplifier and in most cases, one that will drive a full-range signal.
Understanding Amplifier Stereo Separation
 The stereo separation specification is supplied in decibels and describes the amplitude of the signal produced in the adjacent channel. For example, if we have a stereo amp, and we feed a sine wave into the left channel, some of that signal will be reproduced by the right channel. The stereo separation specification tells us how much quieter the signal will be. A good number would be something about 70 dB.
The stereo separation specification is supplied in decibels and describes the amplitude of the signal produced in the adjacent channel. For example, if we have a stereo amp, and we feed a sine wave into the left channel, some of that signal will be reproduced by the right channel. The stereo separation specification tells us how much quieter the signal will be. A good number would be something about 70 dB.
A criterion required to better explain the application of this stereo separation value is to specify at what frequency the signal is tested. In most cases, you’ll see 1 kHz as the specified test frequency. The reason that the frequency needs to be specified is that some amplifiers, in fact, most amplifiers, have more crosstalk (signal leakage from one channel to the other) at higher frequencies.
Why Is Stereo Separation Important?
 When trying to recreate a musical experience, one of the many criteria that people will quantify subjectively is stage width. If you are using an amplifier with a poor stereo separation spec, content from the left channel will be reproduced on the right output and vice versa. This has the effect of making the signal more monaural and effectively reducing the width of the soundstage. If you switch to an amplifier with amazing separation performance, the stage may seem to be wider.
When trying to recreate a musical experience, one of the many criteria that people will quantify subjectively is stage width. If you are using an amplifier with a poor stereo separation spec, content from the left channel will be reproduced on the right output and vice versa. This has the effect of making the signal more monaural and effectively reducing the width of the soundstage. If you switch to an amplifier with amazing separation performance, the stage may seem to be wider.
Measuring Stereo Separation
To give you an idea of how a good amplifier compares with an inexpensive solution, we set up our QuantAsylum QA401 on the bench and took some measurements.
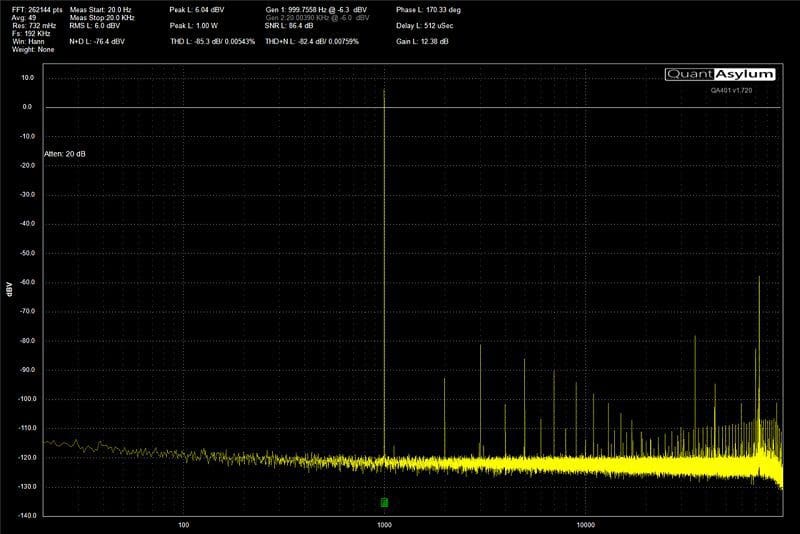
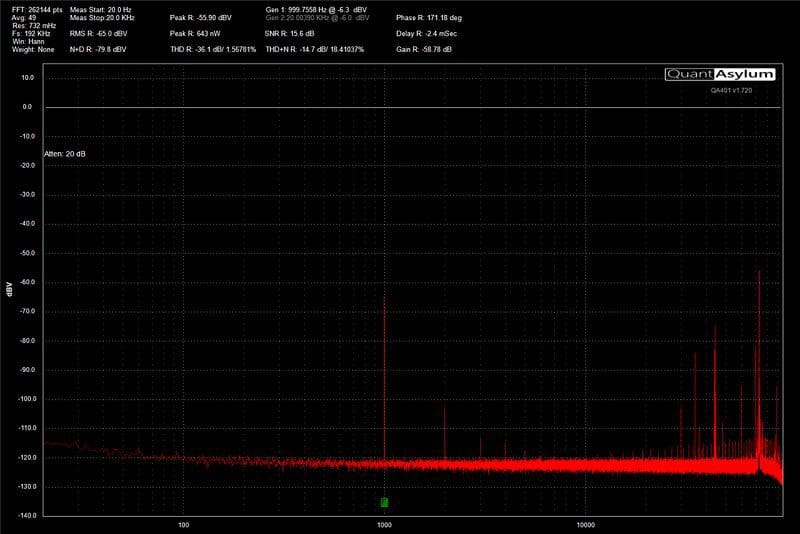
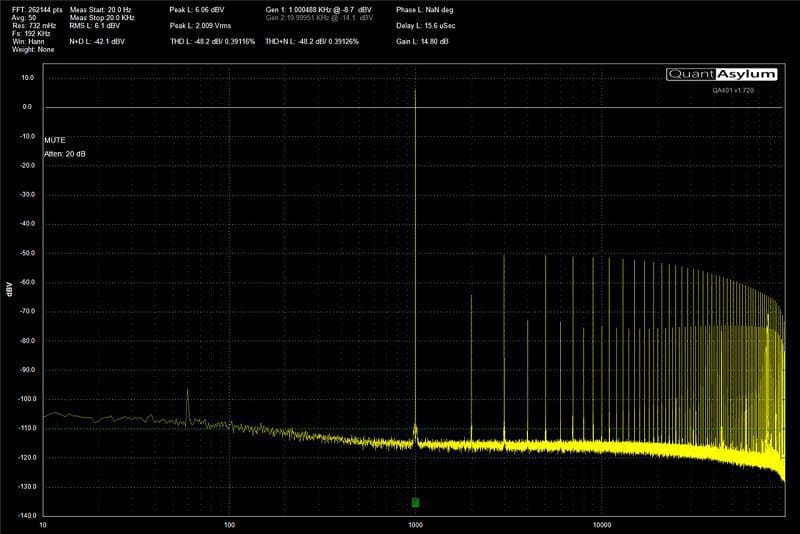
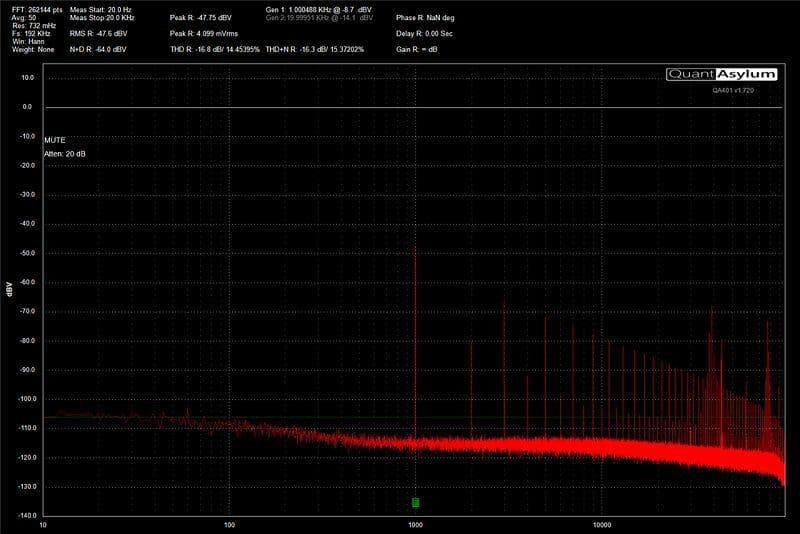
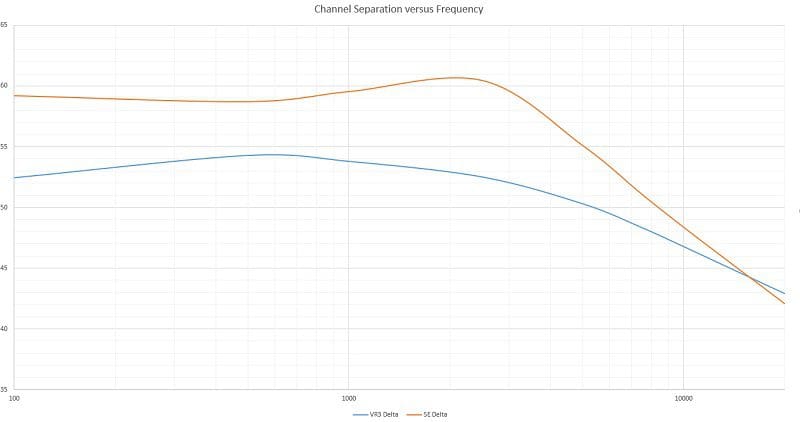
Stereo Separation and Frequency
As we mentioned, crosstalk and channel separation get worse as frequency increases. We took a series of measurements for each of the amplifiers in this test and plotted their channel separation versus frequency in the chart below.
The graph clearly shows that the signal leakage from one channel to another is very dependent on frequency. At 20 kHz, our low-quality amplifier outperforms the good amp. Since we can’t hear 20 kHz, this isn’t an issue.
What to Look for When Shopping for a Car Audio Amplifier
Very few manufacturers publish an amplifier channel separation specification. If you do find a spec, the higher the number, the better the amp will perform in terms of creating a wide soundstage in your vehicle. Your local mobile electronics retailer can help you choose a great amplifier solution and install it for optimum performance and reliability.