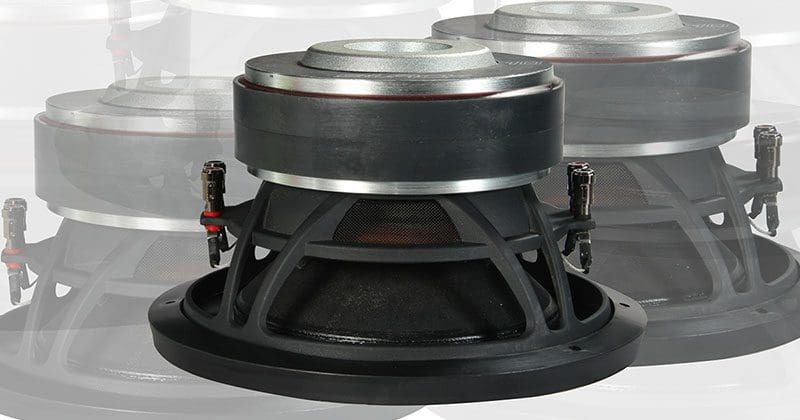
A while back, we took a look at the difference between single and dual-voice-coil subwoofers. In a nutshell, there is no benefit or drawback to either choice. The options exist so you can present the amplifier you have chosen with a load impedance that allows it to make power reliably. There have been many instances where consumers bring a subwoofer into a car stereo shop in hopes of using it in their vehicle only to find out it’s not the right impedance. They need a 4-ohm sub instead of a dual 4-ohm. The question then becomes, can you use just one of the voice coils? That’s a fair question, and it deserves a detailed answer.
Can You Use Only One Subwoofer Voice Coil?
If you look at the voice coil former and the winding of a single-voice-coil sub, you’ll find a single positive and negative connection. On a dual-voice-coil sub, there are two pieces of wire and two sets of connections. The coils can be wired in series, in parallel or individually to power the subwoofer.
Car audio installers can use a set of specifications called Thiele/Small parameters in conjunction with modeling software to predict the performance of a subwoofer in a specific enclosure. All subwoofer manufacturers provide these specifications with both coils in use.
The short answer about using one coil is no. Using one coil not only affects the thermal power handling capabilities of a subwoofer, but it also changes the strength of the magnetic field and alters the Thiele/Small specifications. Rather than explain the math involved in the change, let’s use an example.

Thiele/Small Parameter Changes
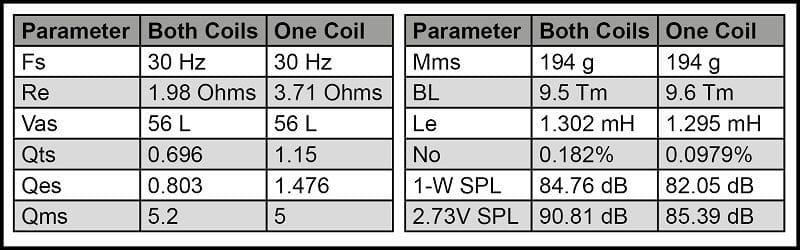
Let’s start by measuring the parameters of an inexpensive 12-inch dual-voice-coil subwoofer. We measured the subwoofer with both coils wired in parallel, then we disconnected one coil and repeated the test. The results are in the chart below:
Sealed Enclosure Performance
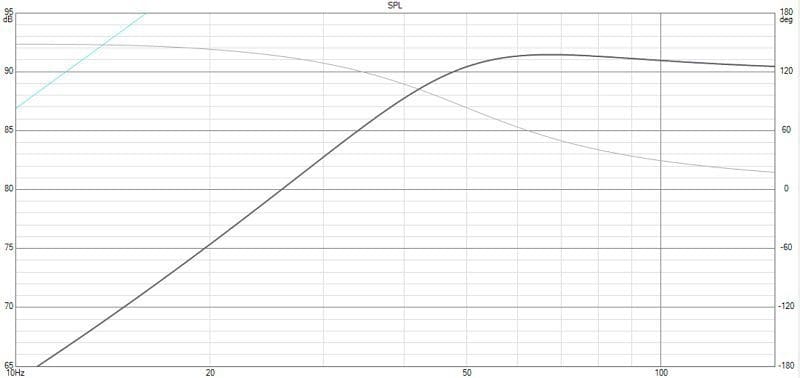
We modeled the subwoofer performance using both voice configurations in VituixCAD 2 software. We started with a simple sealed (acoustic suspension) enclosure with a net internal volume of 1.08 cubic feet. Graph 1 shows the output of the subwoofer with 2.83 V (which is 8-watts into a 4-ohm load) applied to the coil. The response is nice and smooth, with a good transition from the midbass region and very little ripple. The Qtc (Total Q Factor) for the system with both coils connected is 0.8. This is a good balance between low-frequency extension, efficiency and low-distortion operation. The black trace that slopes down on the left shows predicted SPL.
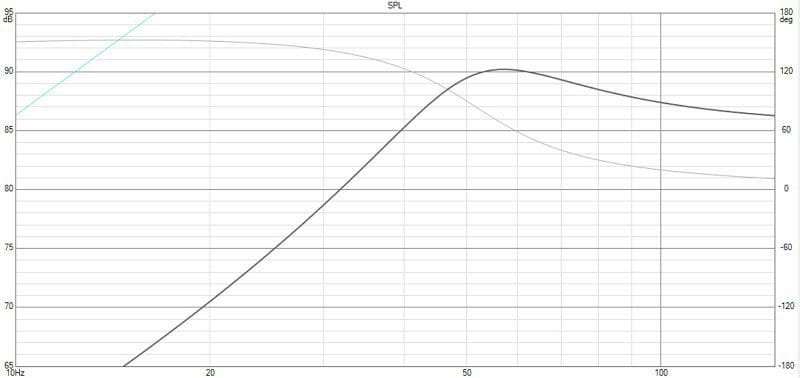
Graph 2 shows the response of the same driver when only one voice coil is connected. You can see that the overall output of the system has decreased significantly and that there is a lot more ripple (a big bump in the response around 57 Hz. It’s also worth noting that the total system Q has jumped to 1.18. This Qtc value is quite high and will add resonance and distortion to the system.
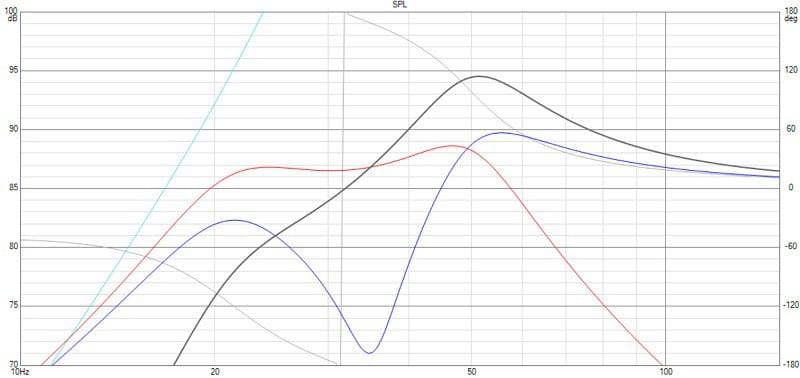
Vented Enclosure Performance
Next, we designed a vented (bass reflex) enclosure using the specs taken with both coils in parallel. We simulated a 2-cubic-foot enclosure with a vent tuned to 35 Hz. As you can see from Graph 3 below, using both voice coils results in relatively smooth performance across the entirety of the operating range. The system efficiency has increased dramatically as compared to the sealed enclosure, with a jump in predicted output from 87 dB to 94 dB with the same amount of power.
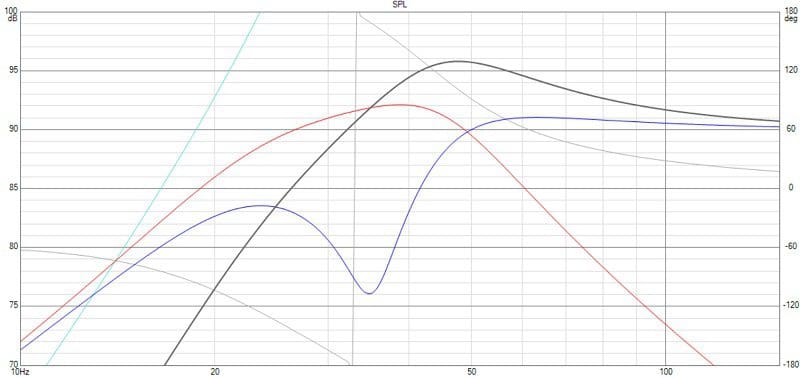
Finally, we can see in Graph 4 how poor the performance of the subwoofer is with only one coil connected. Output at 40 Hz has dropped by 4.5 dB, and the overall response definitely isn’t as smooth.
Make Sure Your Subwoofers are Wired Properly
The above simulations clearly demonstrate the importance of using car audio subwoofers as they were designed. Your installer will need to wire both voice coils to your amplifier to ensure that the subwoofer maintains its power rating and functions the way the manufacturer designed it. If you have any questions, work with your local specialty mobile enhancement retailer.

