If you’ve looked at an amplifier installation kit, you’ll see it comes with about 17 feet of power wire, a shorter length of ground wire and a fuse holder. The intent of this fuse holder is for it to be installed as close as possible to the positive battery terminal. As for the fuse size, should it be the same as the fuse in your amplifier? Likely not. Read on to learn why.
Overcurrent Protection Devices
When it comes to overcurrent protection devices in car audio systems, there are two main contenders: circuit breakers and fuses. Our extensive testing has revealed that circuit breakers, while effective, tend to waste a bit more voltage than their fuse counterparts. Moreover, there’s a risk of circuit breakers not opening when an overcurrent condition occurs. That’s why we strongly advocate using ANL and Mini-ANL fuses to safeguard our vehicles.
A fuse is a simple device in that it’s a piece of metal with a specific area through which all the current going to the load passes. We know that all conductors, be they copper, aluminum or an alloy, have a specific resistance for a given area. As such, fuses are sized so that their resistance will cause the fuse to melt when the current flowing through the device exceeds a certain threshold. Once melted, the current no longer flows to the load.

Why Do We Need a Fuse at the Battery?
When a local mobile enhancement retailer upgrades our vehicle with an amplifier, they run a large-gauge power wire to the battery’s positive terminal and ground the amp’s negative terminal to the chassis. In some cases, especially in vehicles built with aluminum or adhesives, the negative terminal must also go to the battery. The purpose of the fuse is to protect the battery from an overcurrent condition.
What could cause an overcurrent condition in the amplifier power wire? Well, if the wire comes loose from the amp and drops onto the vehicle’s body or touches the negative terminal, a lot of current will flow. Without a fuse, the wire will likely heat up quickly, the jacket will melt, and there could be a fire. Likewise, if the power wire is run across a sharp edge like a hole drilled in a piece of metal, that could cut into the wire and potentially short the wire to the ground. If you’re in an accident where the side of the vehicle is crushed, the power wire might be pinched by the folded metal and be shorted to the ground. Any of these conditions will result in a mess if no overcurrent protection device is installed at the battery.
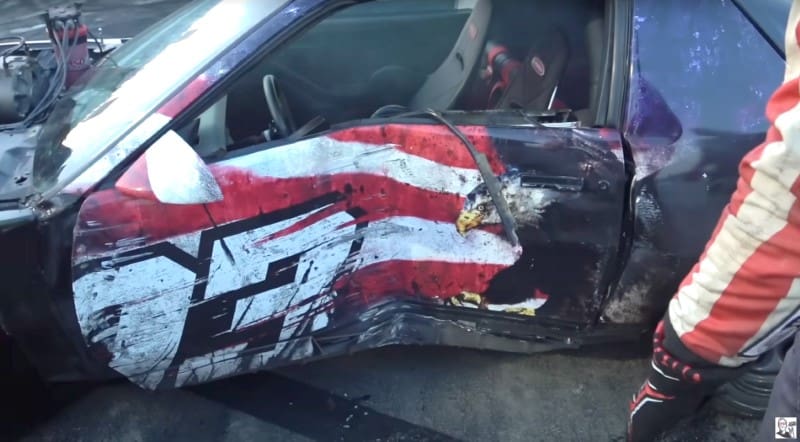

Why Are There Fuses in Car Audio Amplifiers?
Contrary to popular belief, a fuse in a car audio amplifier isn’t to protect the amplifier. Fuses are there to protect the vehicle battery in the event the positive and negative power connections to the amplifier are reversed. Because of how the switching devices in a power supply work, there will be a short circuit if the power connections are reversed. With no protection device, the switching devices will explode violently. The fuse or fuses are not going to prevent damage to the amp if a single switching device fails during regular operation.
So, how are the fuses on an amplifier chosen regarding their current capacity? They need to be large enough to ensure that the amplifier can produce its full rated power without them blowing. We’ve tested a few amplifiers that will pop the included fuses when all channels on the amp are driven at full power into their minimum impedance with test tones. This scenario is different from playing music, so it’s not an issue.
What Size Fuse at the Battery?
To recap, the fuses on the amp protect it from catastrophic failure in the event of a wiring accident. What size should the fuse be at the battery, and what’s its purpose? The fuse at the battery protects the power wire. As such, it should be sized to prevent the wire from carrying more current than it can handle without overheating.
We know there are many official wire sizes, and that wire should be made of copper. However, we also know that there are many mystery wire diameters and that many inexpensive amplifier installation kits use copper-clad aluminum wire. Unfortunately, we don’t know how much aluminum is in these kits, so an educated assessment of the wire resistance is impossible.
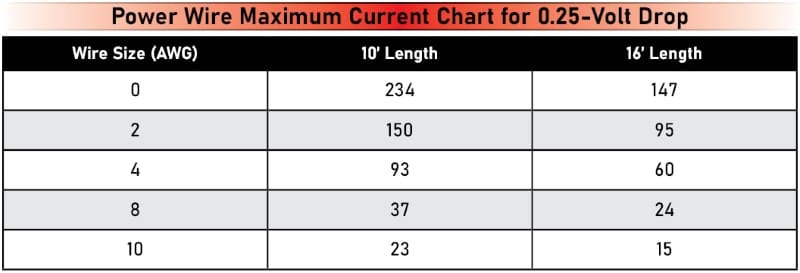
The ANSI/CTA-2015 standard for car audio power wiring suggests we should have no more than 0.25 volt of drop across the wire. This will, of course, be for steady-state current requirements. Nevertheless, we’ll use it as a reference for our calculations. In terms of power wire length, we will provide data for 10- and 16-foot runs. Ten feet is likely adequate to connect an amplifier mounted under a seat to the battery under the hood. Sixteen feet is usually enough to mount an amp in the trunk. The table below shows the maximum current the wire can pass for the given lengths, resulting in a roughly 0.25- to 0.26-volt drop.
As you can see, the maximum current decreases with length. This is because the resistance increases, which results in more voltage drop.
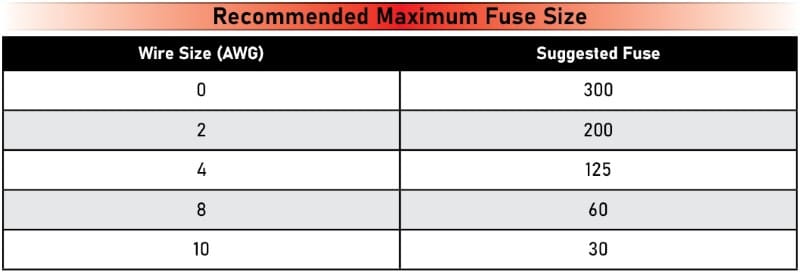
While the above chart is logical, it is perhaps too optimistic about the reality of modern car audio system design. We know of many systems where a run of 4 AWG wire is subjected to well over 100 amps of current. Sure, the amp won’t see the full battery or alternator voltage, but the cable doesn’t melt and catch fire. So, here’s our recommended maximum fuse size chart.
Why Not Use a Smaller Battery Fuse?
Could you use a smaller battery fuse than we’ve recommended? Absolutely. However, there’s an interesting reason why you might not want to. As mentioned, fuses have a specific resistance that causes them to blow when a specific amount of current passes through them. Fuses rated for larger amounts of current have less resistance. As such, less voltage drops across the fuse, and more is available to feed the amplifier. More voltage will result in the amplifier being able to produce more power before it starts clipping.
Fuse Location
Decades ago, the International AutoSound Challenge Association established a rule that said the fuse in a car audio system should be within 14 inches of the battery. Sadly, many people took this to mean that the fuse should be 14 inches from the battery. In reality, the fuse should be as close as possible to the positive terminal to provide maximum protection. Having a fuse 10 to 12 inches away might not provide adequate protection in a front-end collision.
We like the idea of fuse holders that are integrated directly into battery terminals. This design provides the most protection possible should something go wrong.

Ensure that Your Car Audio System Is Protected
While most professional car audio installers know how to adequately protect your vehicle from damage because of a short-circuited power wire, some might need guidance. Before you let anyone work on your vehicle, discuss what type of overcurrent protection device will be used and where it will be installed. A proper battery fuse is crucial to preventing additional damage should something go wrong.